Understanding Laravel MVC Architecture: A Beginner’s Guide
Laravel, a popular PHP framework, relies heavily on the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture. This architectural pattern provides a structured way to organize your code, making it easier to maintain, test, and scale your web applications. This beginner-friendly guide will break down the Laravel Model View Controller Architecture, explaining its core components and how they work together.
What is MVC Architecture?
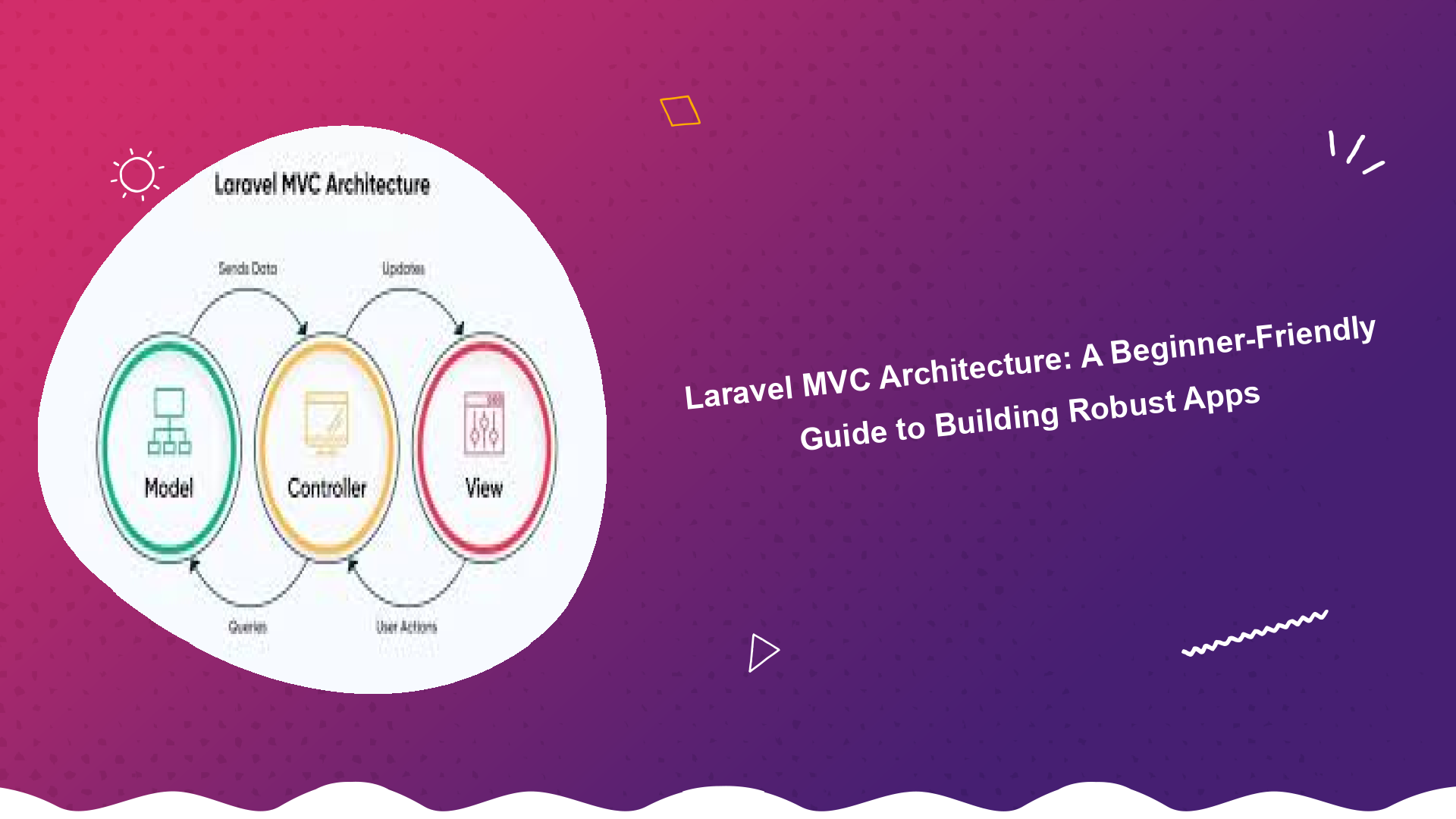
MVC is a software design pattern that separates an application into three interconnected parts: the Model, the View, and the Controller. Each component has a specific responsibility:
- Model: Represents the data of the application and handles data logic. It interacts with the database, retrieves data, and performs data manipulation. Think of it as the heart of your application’s data.
- View: Displays the data to the user. It’s responsible for rendering the user interface, presenting information in a user-friendly format. Views typically contain HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Controller: Acts as an intermediary between the Model and the View. It receives user requests, interacts with the Model to retrieve or update data, and then passes that data to the View for display.
Why Use MVC Architecture in Laravel?
Using the Laravel Model View Controller Architecture offers several significant advantages:
- Organization: MVC provides a clear structure for your code, making it easier to understand and maintain.
- Reusability: Components can be reused across different parts of the application, reducing code duplication.
- Testability: Each component can be tested independently, making it easier to identify and fix bugs.
- Scalability: MVC facilitates building scalable applications by separating concerns and promoting modularity.
- Collaboration: MVC makes it easier for developers to work together on the same project.
The Components of Laravel MVC Architecture
Let’s take a closer look at each component in the context of Laravel:
1. Models
In Laravel, Models typically represent database tables. They are responsible for interacting with the database through Eloquent, Laravel’s ORM (Object-Relational Mapper). Eloquent provides a convenient way to query the database, create new records, update existing records, and delete records.
Here’s a simple example of a Laravel Model:
namespace AppModels;
use IlluminateDatabaseEloquentModel;
class User extends Model
{
// Table name (optional, defaults to pluralized class name)
// protected $table = 'users';
// Fillable attributes (allowed to be mass-assigned)
protected $fillable = ['name', 'email', 'password'];
}
2. Views
Views in Laravel are typically Blade templates, which are files with a `.blade.php` extension. Blade provides a simple and powerful way to define your application’s user interface using templating directives such as `@if`, `@foreach`, and `@extends`. These directives make it easier to inject data into your views and create dynamic content.
Example of a Blade view (resources/views/users/index.blade.php):
<html>
<body>
<h1>Users</h1>
<ul>
@foreach ($users as $user)
<li>{{ $user->name }}</li>
@endforeach
</ul>
</body>
</html>
3. Controllers
Controllers in Laravel handle incoming HTTP requests. They receive the request, interact with the Model to retrieve or update data, and then pass that data to the View. Controllers act as the glue between the Model and the View.
Here’s an example of a Laravel Controller:
namespace AppHttpControllers;
use AppModelsUser;
use IlluminateHttpRequest;
class UserController extends Controller
{
public function index()
{
$users = User::all();
return view('users.index', compact('users'));
}
}
Laravel MVC Directory Structure
Understanding the directory structure is key to mastering the Laravel Model View Controller Architecture. Here’s a breakdown of the key directories:
- app/Models: Contains your application’s Eloquent models.
- app/Http/Controllers: Contains your application’s controllers.
- resources/views: Contains your application’s Blade templates (views).
- routes: Contains your application’s route definitions, which map URLs to controllers.
How the MVC Flow Works in Laravel
Let’s trace the flow of a typical request in a Laravel MVC application:
- The user sends a request to a specific URL.
- The Router, defined in the `routes` directory, matches the URL to a specific Controller action.
- The Controller action executes.
- The Controller interacts with the Model to retrieve or update data.
- The Controller passes the data to the View.
- The View renders the data and returns the HTML response to the user.
Implementing MVC Architecture in Laravel: A Simple Example
Let’s create a simple example to illustrate the Laravel Model View Controller Architecture. We’ll create a page that displays a list of blog posts.
- Create a Model: Create a `Post` model representing the `posts` table in your database.
- Create a Controller: Create a `PostController` with an `index` action that retrieves all posts from the database and passes them to the view.
- Create a View: Create a `posts/index.blade.php` view that displays the list of posts.
- Define a Route: Define a route in `routes/web.php` that maps the `/posts` URL to the `PostController@index` action.
By following these steps, you’ll have a basic application that demonstrates the core principles of the Laravel Model View Controller Architecture.
Best Practices for Using MVC in Laravel
- Keep your controllers thin: Avoid putting too much logic in your controllers. Move complex business logic to services or repositories.
- Use Eloquent relationships: Leverage Eloquent’s relationships to easily manage data relationships between different models.
- Use form requests: Use form requests to validate user input and ensure data integrity.
- Use middleware: Use middleware to handle tasks such as authentication, authorization, and logging.
- Write tests: Write unit tests and feature tests to ensure that your code is working correctly.
Conclusion
The Laravel Model View Controller Architecture is a powerful tool for building robust and maintainable web applications. By understanding the core components of MVC and following best practices, you can create high-quality applications that are easy to understand, test, and scale. Remember to leverage Laravel’s built-in features, such as Eloquent and Blade, to streamline your development process.
For more in-depth learning, consider exploring the official Laravel documentation (https://laravel.com/docs/) and online tutorials. You can also learn more about web development concepts from reputable sources like Mozilla Developer Network (https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/) and freeCodeCamp (https://www.freecodecamp.org/).
Continue learning and experimenting, and you’ll quickly become proficient in building Laravel applications using the MVC architecture.
Want to learn more about clean PHP code practices? Check out this article on writing readable PHP code examples.
Interested in learning more about secure user management in Laravel? check out the laravel user authentication tutorial
For those looking to build REST APIs, here’s a laravel rest api development tutorial