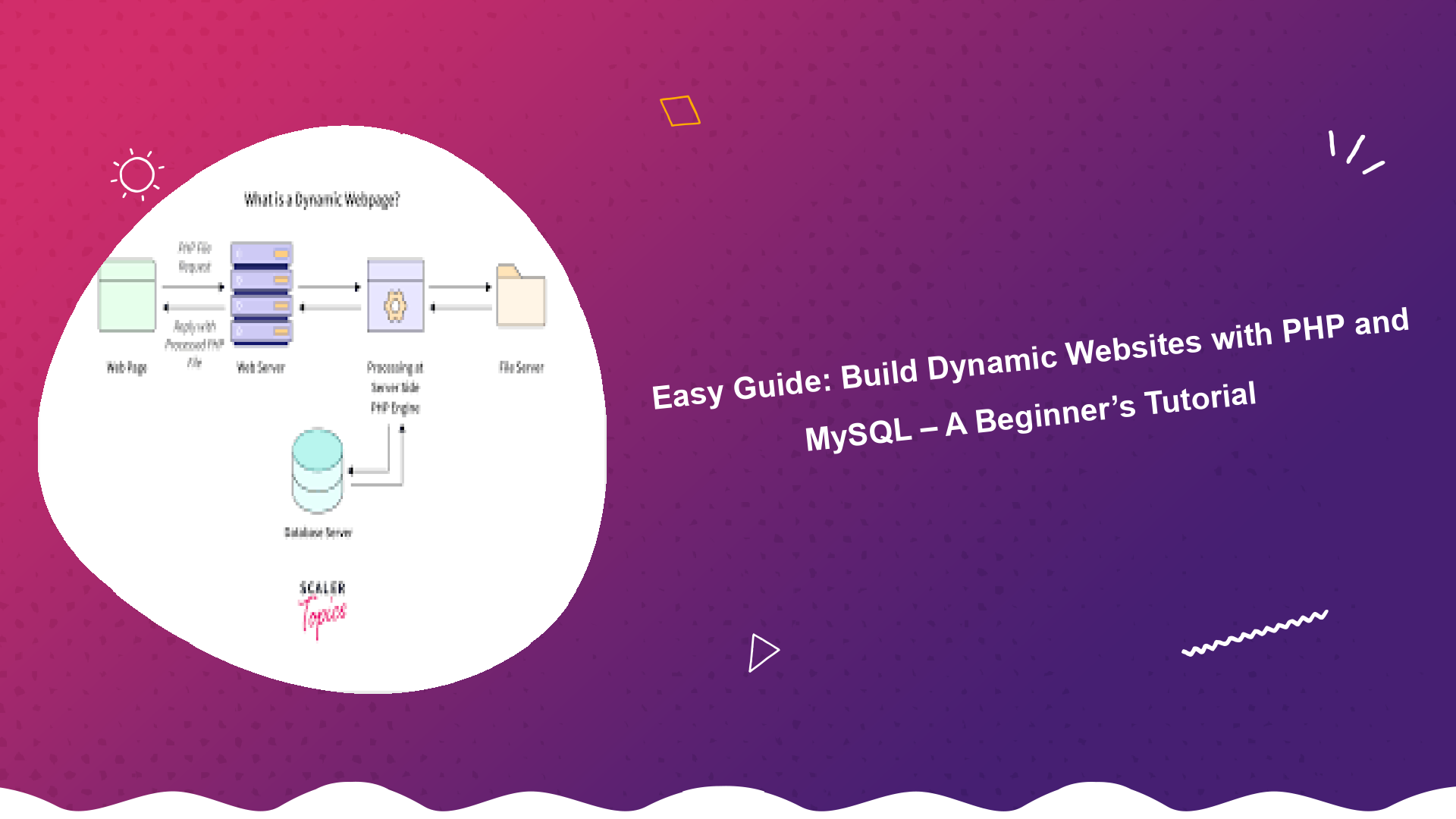
Introduction to Building Dynamic Websites with PHP and MySQL
Are you looking to create interactive and engaging websites that adapt to user input? This easy guide will walk you through the process of building dynamic websites with PHP and MySQL. This tutorial is perfect for beginners eager to learn the fundamentals of web development. Creating a dynamic website with PHP and MySQL is easier than you might think! Let’s dive in.
A dynamic website, unlike a static one, changes its content based on user interactions, database updates, or other factors. This allows for personalized experiences, user accounts, e-commerce functionality, and much more. The combination of PHP, a server-side scripting language, and MySQL, a powerful database management system, provides the perfect foundation for building robust and scalable dynamic web applications.
Setting Up Your Development Environment
Before we start coding, we need to set up a suitable development environment. This typically involves installing a web server, PHP, and MySQL on your local machine. Fortunately, there are convenient software packages like XAMPP, WAMP, and MAMP that bundle all these components together.
Installing XAMPP (Recommended)
XAMPP is a free and open-source cross-platform web server solution stack package, consisting mainly of the Apache HTTP Server, MySQL database, and interpreters for scripts written in the PHP and Perl programming languages. Download the correct version for your operating system from Apache Friends.
- Download XAMPP from the official website.
- Run the installer and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Start the Apache and MySQL modules from the XAMPP Control Panel.
Understanding PHP Basics
PHP is a server-side scripting language that allows you to embed code within HTML pages. This code is executed on the server, generating dynamic content that is then sent to the user’s browser. Understanding the basics of PHP is crucial for building dynamic websites with PHP and MySQL.
PHP Syntax
PHP code is enclosed within <?php ?> tags.
<?php
echo "Hello, World!";
?>Variables and Data Types
PHP supports various data types, including strings, integers, floats, booleans, and arrays.
<?php
$name = "John"; // String
$age = 30; // Integer
$price = 99.99; // Float
$is_active = true; // Boolean
echo "Name: " . $name . "<br>";
echo "Age: " . $age . "<br>";
?>Control Structures
PHP provides control structures like if, else, for, while, and switch to control the flow of execution.
<?php
$score = 75;
if ($score >= 60) {
echo "Passed!";
} else {
echo "Failed!";
}
?>Introduction to MySQL Databases
MySQL is a relational database management system (RDBMS) that allows you to store and manage structured data. This is essential for building dynamic websites with PHP and MySQL because the website can pull information and interact with user input.
Creating a Database
You can create a database using a tool like phpMyAdmin, which is included with XAMPP. Log in to phpMyAdmin (usually at http://localhost/phpmyadmin) and create a new database.
Creating Tables
Tables are used to organize data within a database. Each table consists of columns and rows. Create a table using SQL (Structured Query Language).
CREATE TABLE users (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
username VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
password VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE NOT NULL
);Connecting PHP to MySQL
To interact with the MySQL database from your PHP code, you need to establish a connection. This can be done using the mysqli extension in PHP. Securing your PHP and MySQL connection is paramount. Always sanitize user input to prevent SQL injection attacks. You can learn more about security best practices from resources like the OWASP Top Ten.
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = ""; // Change this in a real application!
$database = "your_database";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $database);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
echo "Connected successfully";
?>Performing CRUD Operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete)
CRUD operations are the fundamental operations you can perform on a database.
Creating (Inserting) Data
<?php
$username = "newuser";
$password = password_hash("password", PASSWORD_DEFAULT); // Hash the password!
$email = "newuser@example.com";
$sql = "INSERT INTO users (username, password, email) VALUES ('$username', '$password', '$email')";
if ($conn->query($sql) === TRUE) {
echo "New record created successfully";
} else {
echo "Error: " . $sql . "<br>" . $conn->error;
}
?>Reading (Selecting) Data
<?php
$sql = "SELECT id, username, email FROM users";
$result = $conn->query($sql);
if ($result->num_rows > 0) {
// Output data of each row
while($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) {
echo "ID: " . $row["id"]. " - Username: " . $row["username"]. " - Email: " . $row["email"]. "<br>";
}
} else {
echo "0 results";
}
?>Updating Data
<?php
$id = 1; // ID of the record to update
$new_email = "updated@example.com";
$sql = "UPDATE users SET email='$new_email' WHERE id=$id";
if ($conn->query($sql) === TRUE) {
echo "Record updated successfully";
} else {
echo "Error updating record: " . $conn->error;
}
?>Deleting Data
<?php
$id = 1; // ID of the record to delete
$sql = "DELETE FROM users WHERE id=$id";
if ($conn->query($sql) === TRUE) {
echo "Record deleted successfully";
} else {
echo "Error deleting record: " . $conn->error;
}
?>Building a Simple Dynamic Website
Let’s create a basic dynamic website that displays a list of users from the database.
index.php
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Dynamic Website</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>User List</h1>
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "";
$database = "your_database";
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $database);
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$sql = "SELECT id, username, email FROM users";
$result = $conn->query($sql);
if ($result->num_rows > 0) {
echo "<ul>";
while($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) {
echo "<li>" . $row["username"] . " - " . $row["email"] . "</li>";
}
echo "</ul>";
} else {
echo "No users found.";
}
$conn->close();
?>
</body>
</html>Save this code as index.php in your XAMPP htdocs directory (usually C:xampphtdocs on Windows). Access it through your browser by navigating to http://localhost/index.php. You should see a list of users from your database.
Advanced Techniques
Using Prepared Statements
Prepared statements are used to prevent SQL injection attacks. They allow you to separate the SQL code from the data.
<?php
$username = "newuser2";
$password = password_hash("password2", PASSWORD_DEFAULT);
$email = "newuser2@example.com";
$sql = "INSERT INTO users (username, password, email) VALUES (?, ?, ?)";
$stmt = $conn->prepare($sql);
$stmt->bind_param("sss", $username, $password, $email);
if ($stmt->execute()) {
echo "New record created successfully";
} else {
echo "Error: " . $stmt->error;
}
?>Object-Oriented PHP and MySQL
Using object-oriented programming (OOP) principles can make your code more organized and maintainable. Consider using a PHP framework like Laravel for more complex projects. Check out this comparison of Laravel vs Symfony framework before starting a new project. Understanding and utilising PHP Dependency Management with Composer is essential to stay efficient.
Best Practices for Building Dynamic Websites
- Sanitize User Input: Always sanitize user input to prevent SQL injection attacks.
- Use Prepared Statements: Use prepared statements to protect against SQL injection.
- Hash Passwords: Always hash passwords before storing them in the database.
- Proper Error Handling: Implement proper error handling to catch and handle exceptions.
- Regular Database Backups: Regularly back up your database to prevent data loss.
- Optimize PHP code and database queries for faster loading times. Consider implementing a caching strategy like the ones discussed here: Mastering Laravel Caching Strategies
Conclusion
This guide provided a basic introduction to building dynamic websites with PHP and MySQL. As you delve deeper into web development, remember to continuously learn and experiment with new techniques and technologies. Understanding basic Web Development concepts is a continuous process. This allows you to build even more complex and engaging web applications and improve productivity with the best Laravel productivity tools.. With practice and dedication, you can create powerful and interactive web experiences for your users.